 Do you ever wonder what newborns would say if they could talk? Where am I? What just happened? Who turned on the lights? Whew, that was a lot of work! I’m exhausted. Why is everyone staring at me? Do I have something on my face? Mom! Dad! It’s me! Truth is—most newborns all say the same thing: WaaaaWaaaa!
Do you ever wonder what newborns would say if they could talk? Where am I? What just happened? Who turned on the lights? Whew, that was a lot of work! I’m exhausted. Why is everyone staring at me? Do I have something on my face? Mom! Dad! It’s me! Truth is—most newborns all say the same thing: WaaaaWaaaa!
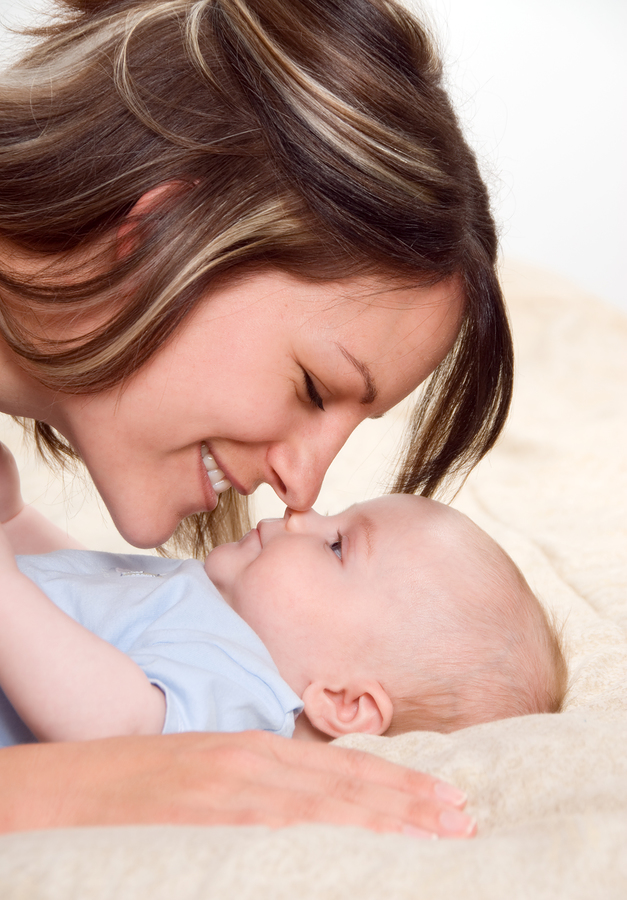
Of course, children aren’t born talking. However, even at birth, a child can usually respond to a mother’s voice, an early sign of communication, Speech and early language development involves both receptive language (what a child hears and understands) and expressive language (what a child says to others through sounds and gestures). Receptive language skills show up first as babies learn to turn towards interesting sounds or respond to tones and even their own names.
New Research: Improving Babies’ Language Skills Before They Can Talk
A new study from Rutgers University indicates that babies can be taught to better recognize sounds that “might” be language. This would increase brain development in the areas responsible for language acquisition and processing.
In the study led by Emily Benasich who directs the Infancy Studies Laboratory at Rutgers University’s Center for Molecular and Behavioral Neuroscience, the team found that when 4-month-old babies learned to pay attention to increasingly complex non-language audio patterns, their brain scans at 7 months old showed they were faster and more accurate at detecting other sounds important to language than babies who had not been exposed to the sound patterns.
“Young babies are constantly scanning the environment to identify sounds that might be language,” explained Benasich in a press release. “This is one of their key jobs – as between 4 and 7 months of age they are setting up their pre-linguistic acoustic maps….If you shape something while the baby is actually building it, it allows each infant to build the best possible auditory network for his or her particular brain. This provides a stronger foundation for any language (or languages) the infant will be learning.”
Take a look inside the Laboratory:
[youtube] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fJ3yZDoRwOs[/youtube]
Use Music to Support Early Language Development
In Kindermusik classes, we provide many opportunities for caregivers and babies to communicate with each other both verbally and nonverbally. For example, when we actively listen to a specific sound such as a clock sound or running water sound, integrate language and movement during a song, or use sign language, babies gain practice hearing words and making connections to their meanings—all which heightens babies’ abilities to communicate!




 Take the story of children attending Kindermusik at Learn & Play in Beirut, Lebanon, for example. Last year this pioneer nursery in Lebanon began offering two Kindermusik curricula:
Take the story of children attending Kindermusik at Learn & Play in Beirut, Lebanon, for example. Last year this pioneer nursery in Lebanon began offering two Kindermusik curricula:  Learn & Play teaches children French, Arabic, and English. Since using ABC English & Me to introduce young children to English as a second language, children can now count, sing, and name different parts of the body using English. Music is a great way to help children become familiar with English and the different visuals and animated stories used in ABC English & Me make it easy for children to interact and learn English.
Learn & Play teaches children French, Arabic, and English. Since using ABC English & Me to introduce young children to English as a second language, children can now count, sing, and name different parts of the body using English. Music is a great way to help children become familiar with English and the different visuals and animated stories used in ABC English & Me make it easy for children to interact and learn English.




 Young children learn best through hands-on, multi-sensory experiences with a loving and trusted caregiver. However, with technology firmly imbedded into the daily lives and routines of families today, parents and early childhood educators often struggle with knowing the ideal ways to incorporate screen time that also supports what we know about how children learn.
Young children learn best through hands-on, multi-sensory experiences with a loving and trusted caregiver. However, with technology firmly imbedded into the daily lives and routines of families today, parents and early childhood educators often struggle with knowing the ideal ways to incorporate screen time that also supports what we know about how children learn.
 “Again! Again!” It is not a coincidence that young children ask to read the same book 22 nights in a row. While the adults involved may secretly (and not so secretly) wish for more diversity, all that repetition strengthens the learning or growth of neural connections in children’s brains.
“Again! Again!” It is not a coincidence that young children ask to read the same book 22 nights in a row. While the adults involved may secretly (and not so secretly) wish for more diversity, all that repetition strengthens the learning or growth of neural connections in children’s brains.
 It’s Halloween! In many parts of the world, this means dressing up in costumes and pretending to be a cowboy, ninja, ballet dancer, or even a cowboy ninja ballet dancer. (Hey, it could happen!) While the stores—and Pinterest—overflow with costume options for children this time of year, truth be told, children love dressing up and pretending all year long. And they should! It’s good for them.
It’s Halloween! In many parts of the world, this means dressing up in costumes and pretending to be a cowboy, ninja, ballet dancer, or even a cowboy ninja ballet dancer. (Hey, it could happen!) While the stores—and Pinterest—overflow with costume options for children this time of year, truth be told, children love dressing up and pretending all year long. And they should! It’s good for them.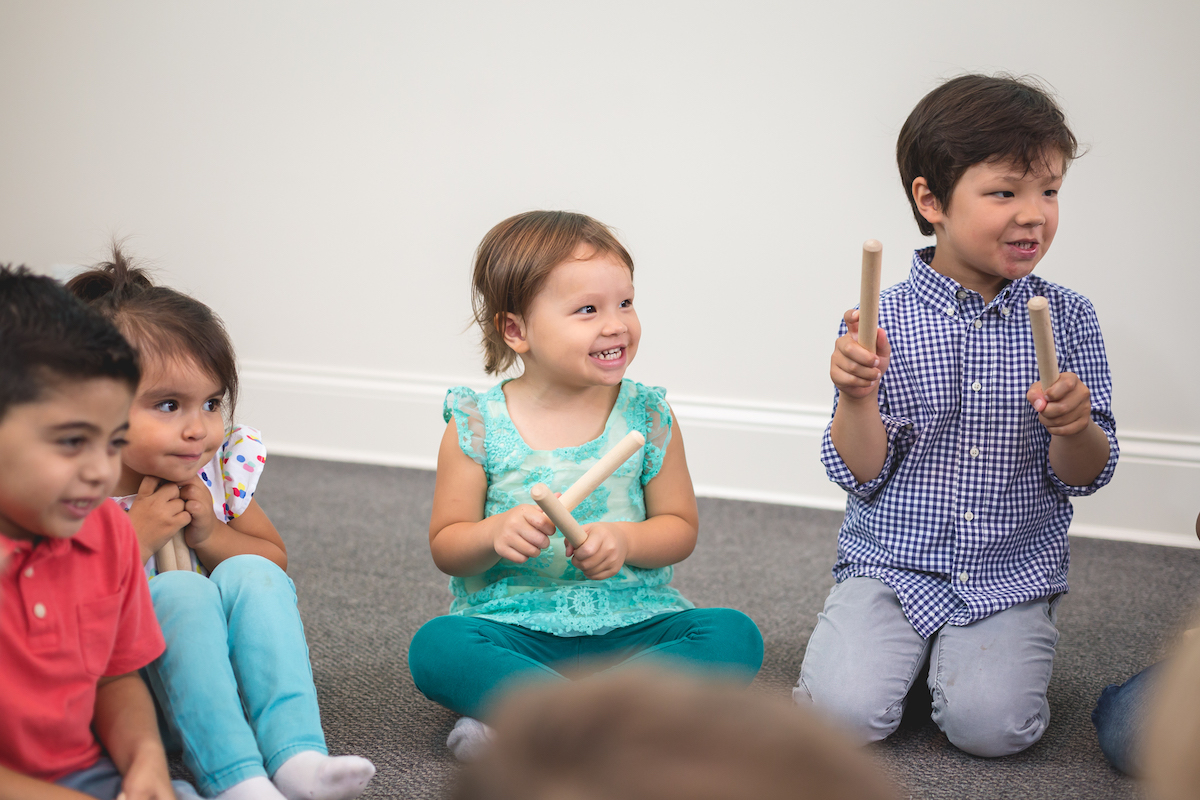

 An
An 
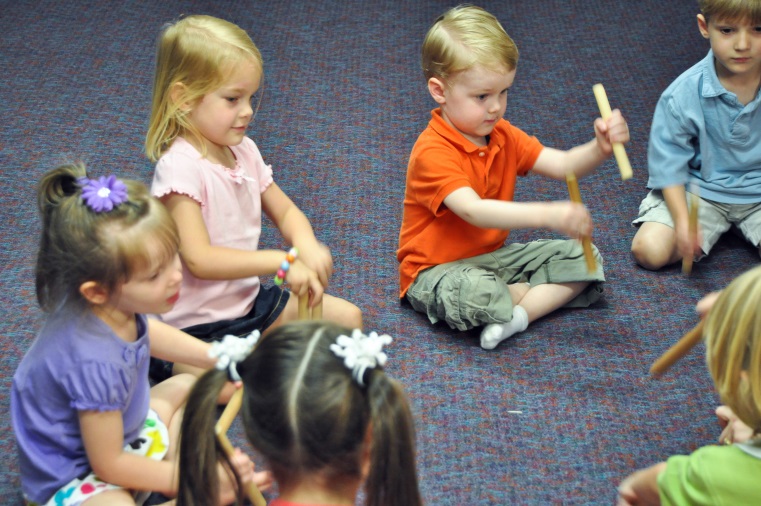
 Here are six music activities that support early language development – all six are favorites of our Kindermusik parents in class and at home:
Here are six music activities that support early language development – all six are favorites of our Kindermusik parents in class and at home: Learn more about how Kindermusik can give you the inspiration you need for improving your child’s language development at
Learn more about how Kindermusik can give you the inspiration you need for improving your child’s language development at