 What do you get when you cross group activities for kids with music and learning? That’s just one of the questions a research team led by Dr. Nina Kraus seeks to answer in two new brain studies funded by the NAMM Foundation. Unlike past research that compares children taking private music lessons to those not enrolled, one unique aspect of Kraus’s latest music and learning research is that it focuses on children learning in a group as part of a school curriculum.
What do you get when you cross group activities for kids with music and learning? That’s just one of the questions a research team led by Dr. Nina Kraus seeks to answer in two new brain studies funded by the NAMM Foundation. Unlike past research that compares children taking private music lessons to those not enrolled, one unique aspect of Kraus’s latest music and learning research is that it focuses on children learning in a group as part of a school curriculum.
“The NAMM Foundation is honored to support Dr. Kraus in these studies, which we believe will push the boundaries of knowledge about the effects and impact of music learning,” said Mary Luehrsen, executive director of the NAMM Foundation in a press release. “Over time, these and other studies will continue to substantiate that music education is essential to learning for every child.”
The Music and Learning Brain Studies led by Dr. Kraus
- “The Harmony Project: Biological Benefits of Musical Training in At-Risk Children.” The initial phase of the research study found that children between the ages of 6 and 9 years old who took music lessons could better differentiate speech sounds, which directly relates to language and literacy skills. In the next phase, the team expects to find that children with musical training have an enhanced auditory cognitive function, which can also directly correlate to increased literacy skills.
- “The Impact of In-School Music Classes: Rhythm, Language and the Brain.” In collaboration with the Chicago Public Schools, Kraus and her team want to better understand how musical training impacts cognitive, linguistic, and perceptual skills and associated brain development.
And the answer is…
So back to the first question (with an added bonus!): What do you get when you cross group activities for kids with music and learning AND parent involvement in early childhood education? Well, Kindermusik, of course! From Kindermusik classes in more than 70 countries around the world to ABC Music & Me programs used as part of an elementary school, PreK, or Head Start curriculum, we use
music as the vehicle for learning. Plus, we include materials that connect the classroom learning with the everyday lives and routines of children to increase family involvement in education.




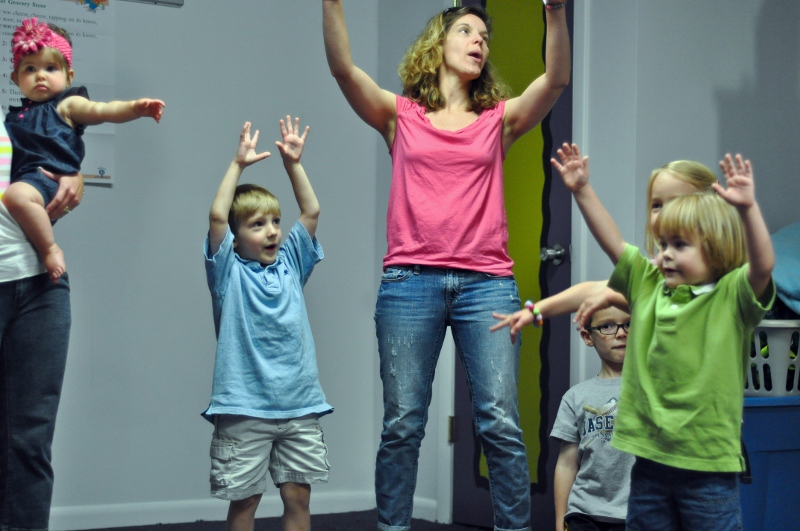


 Early language development begins long before children say recognizable words. Linguist Patricia Kuhl notes that a six-to-eight month old baby can discriminate any sound in any language. In early language development, children naturally learn phonetically by interacting with other people. In contrast, learning another language in later years, such as in high school or at university, often includes many hours of learning through grammar, syntax, and conjugating verbs. Je suis. Tu es. Il est.
Early language development begins long before children say recognizable words. Linguist Patricia Kuhl notes that a six-to-eight month old baby can discriminate any sound in any language. In early language development, children naturally learn phonetically by interacting with other people. In contrast, learning another language in later years, such as in high school or at university, often includes many hours of learning through grammar, syntax, and conjugating verbs. Je suis. Tu es. Il est. Read more about the
Read more about the 

 Regular schedules provide a framework that orders a young child’s world. While predictability can be tedious for adults, children thrive on sameness and repetition. “Knowing what to expect from relationships and activities helps children become more confident,” says Dr. Peter Gorski, assistant professor of pediatrics at Harvard Medical School (Asher).
Regular schedules provide a framework that orders a young child’s world. While predictability can be tedious for adults, children thrive on sameness and repetition. “Knowing what to expect from relationships and activities helps children become more confident,” says Dr. Peter Gorski, assistant professor of pediatrics at Harvard Medical School (Asher).
 Music classes in the early years that include parental involvement and focus on learning in a fun, developmentally appropriate way inspire a lifelong love for learning.
Music classes in the early years that include parental involvement and focus on learning in a fun, developmentally appropriate way inspire a lifelong love for learning.





 Results from teacher surveys indicate that preschool teachers found the ABC Music & Me curriculum to be effective in teaching a variety of skills, and would strongly recommend it to other preschool teachers, and that parents would recommend the program to other parents.
Results from teacher surveys indicate that preschool teachers found the ABC Music & Me curriculum to be effective in teaching a variety of skills, and would strongly recommend it to other preschool teachers, and that parents would recommend the program to other parents.